Permalink🚀 Introduction 🌞:
Kubernetes has emerged as the de facto standard for container orchestration, allowing developers to efficiently manage and scale their applications. In this article, we will walk you through the process of hosting a two-tier Flask application using Kubernetes. This setup will consist of a frontend/backend and Database tier, each running in separate containers within a Kubernetes cluster. By the end of this guide, you will have a scalable and resilient architecture for your Flask app.
Permalink🚀Kubernetes Setup:
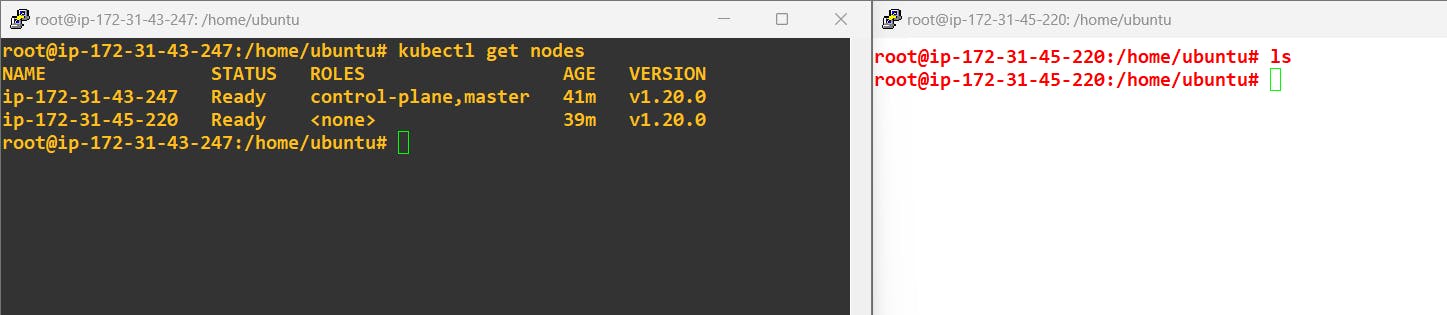
I have already set up a Kubernetes Cluster with master and worker nodes:
Permalink🚀Docker Images:
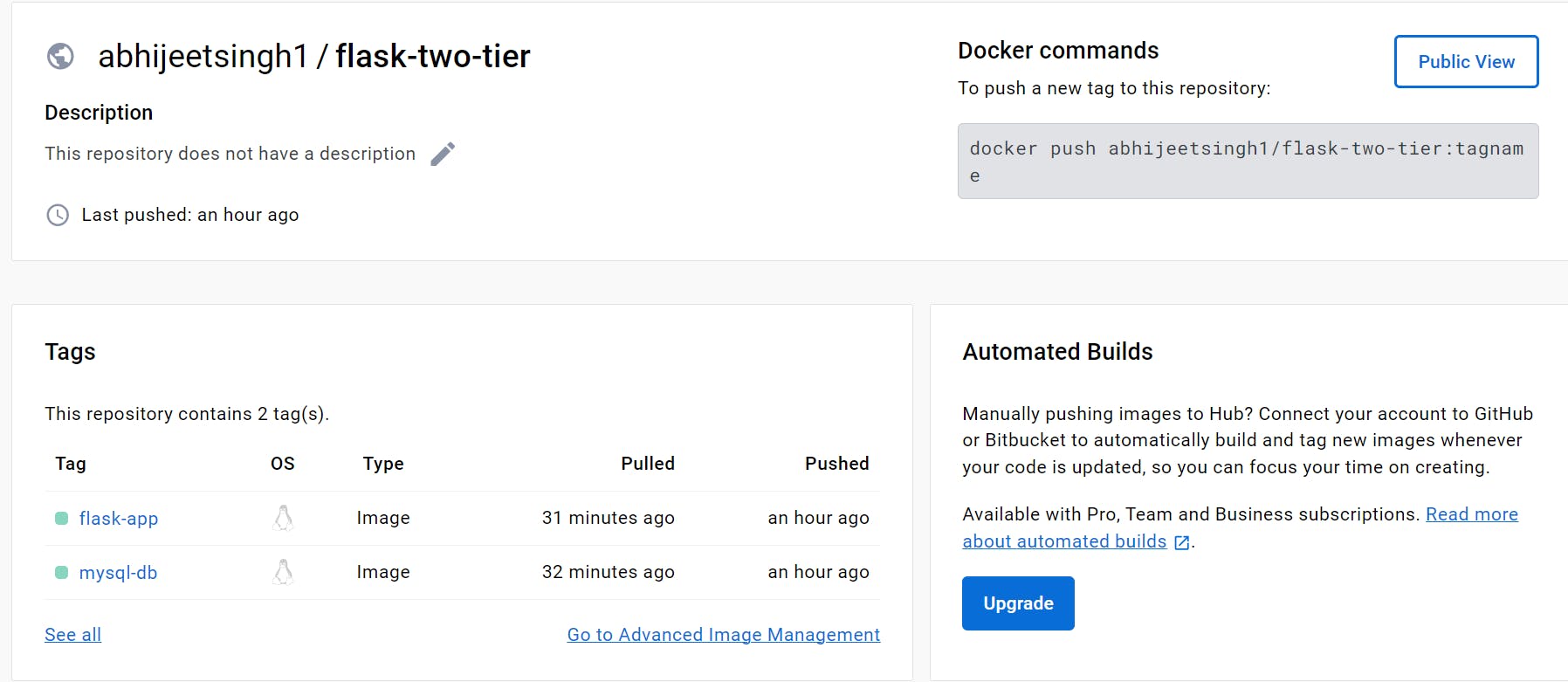
I have already pushed the Docker images into the Docker hub, I will use these images to deploy my application.
Permalink🚀Deploying Your App:
Step-1 Create a Deployment file for MySQL database:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mysql-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mysql
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mysql
spec:
containers:
- name: mysql
image: abhijeetsingh1/flask-two-tier:mysql-db
env:
- name: MYSQL_DATABASE
value: mydatabase
- name: MYSQL_USER
value: user1
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: mypassword
ports:
- containerPort: 3306
Step-2 Creating a Cluster-IP Service for my Database:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mysql-service
spec:
selector:
app: mysql
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 3306
targetPort: 3306
type: ClusterIP
Step-3 Creating a Deployment File for Web app:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: flask-app-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: flask-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: flask-app
spec:
containers:
- name: flask-app
image: abhijeetsingh1/flask-two-tier:flask-app
env:
- name: DB_HOST
value: mysql-service # This is the DNS name of the MySQL ClusterIP Service
- name: DB_PORT
value: "3306" # MySQL default port
- name: DB_USER
value: user1 # Replace with your MySQL username
- name: DB_PASSWORD
value: mypassword # Replace with your MySQL password
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
Step-4 Create a Nodeport Service to expose it to the external world:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: flask-app-nodeport
spec:
selector:
app: flask-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80 # External traffic will be directed to this port
targetPort: 5000 # Matches the containerPort of the Flask app
type: NodePort
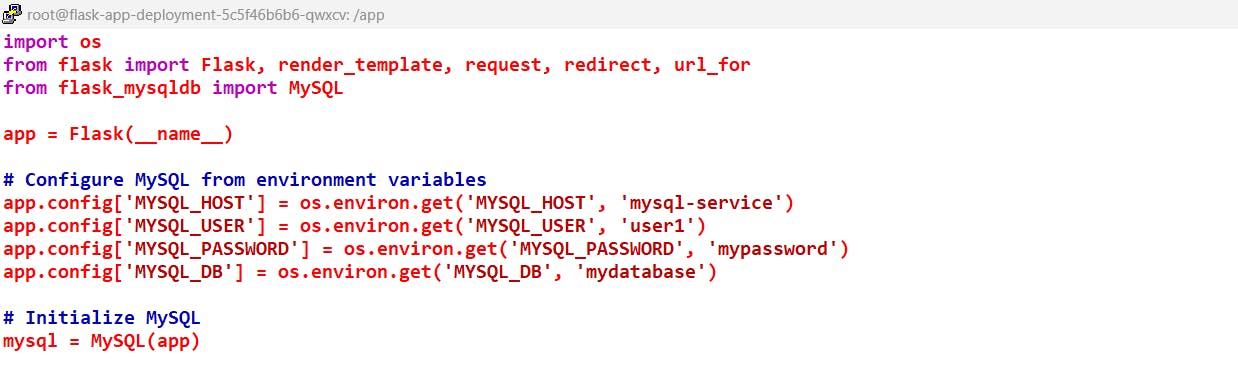
Note: FOR connection between Application and Database I am using DNS Based Service Discovery
Also, set the env in app.py.
Step-5 Now apply all services and Deployment yml file :
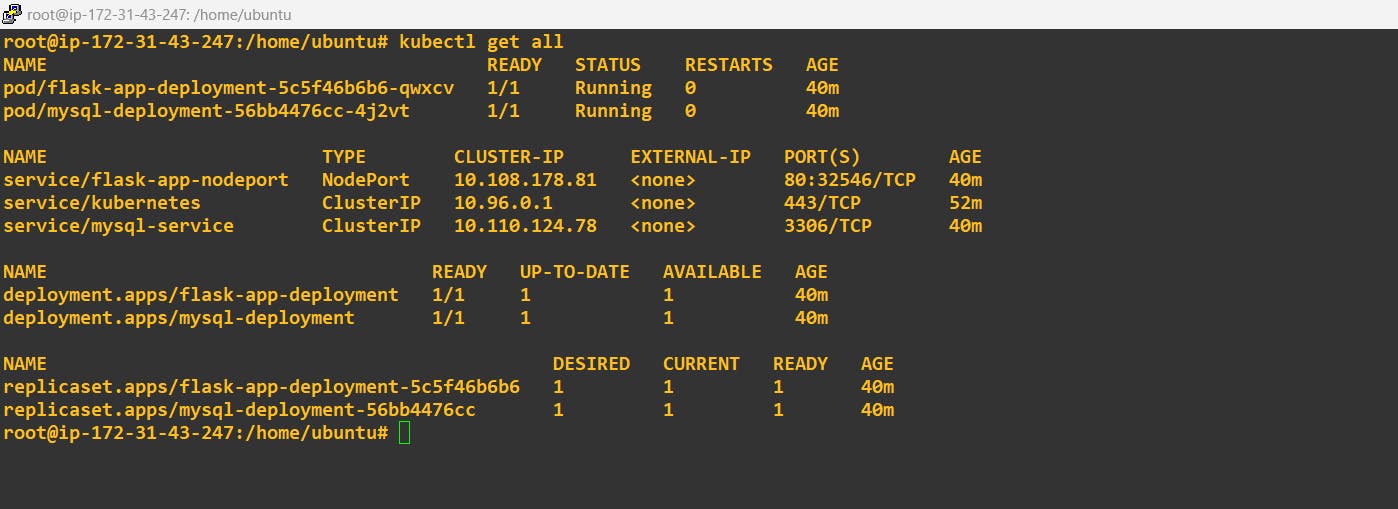
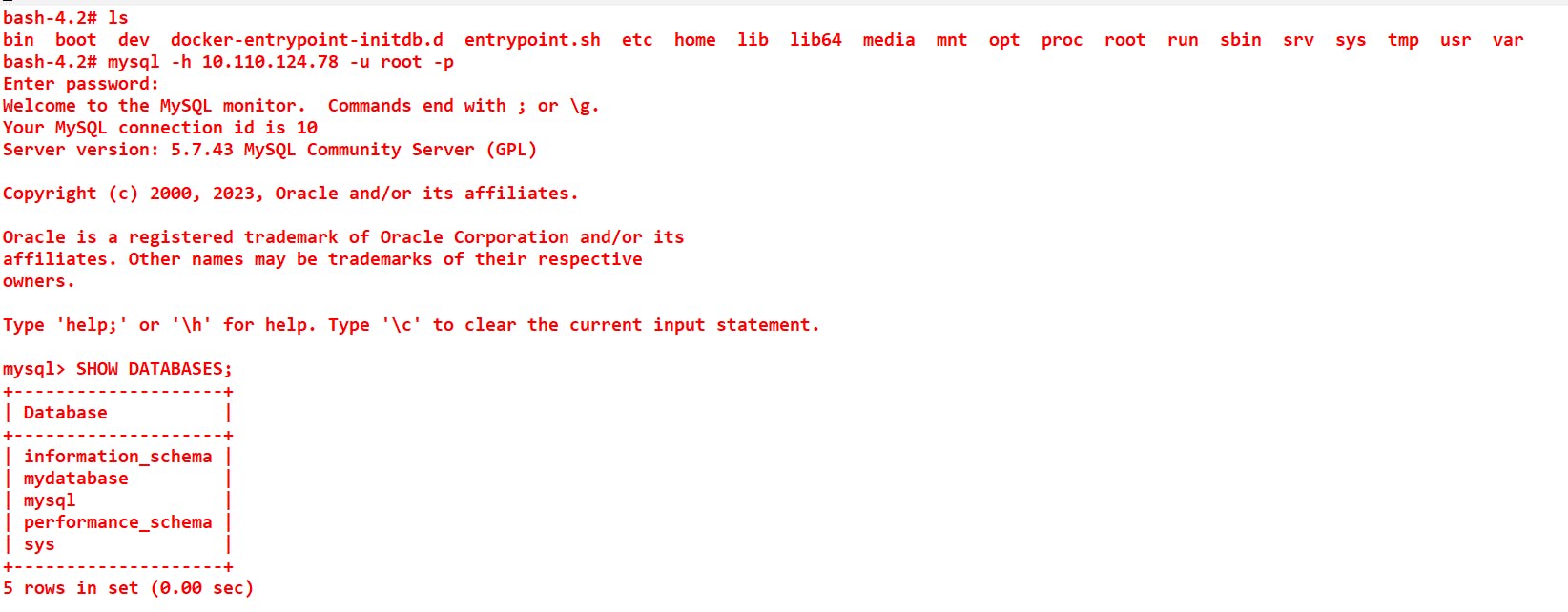
Step-6 Just verify the Database name and user in MySQL:
use Command:
mysql -h 10.110.124.78 -u root -p
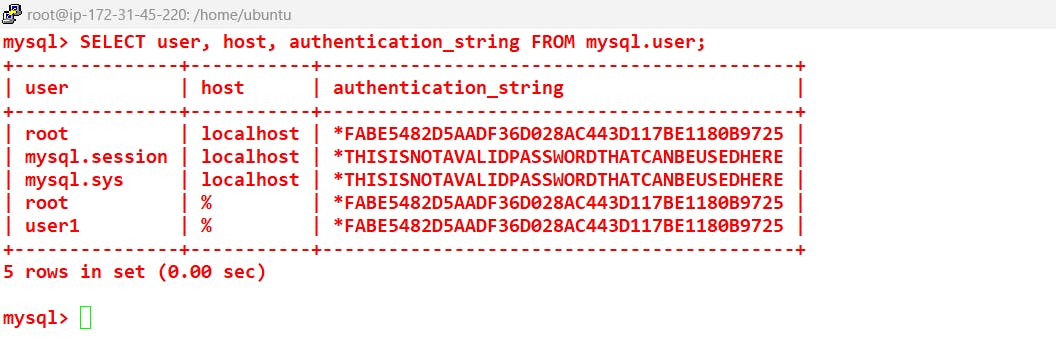
Verify the user that you have created:
SELECT user, host, authentication_string FROM mysql.user;
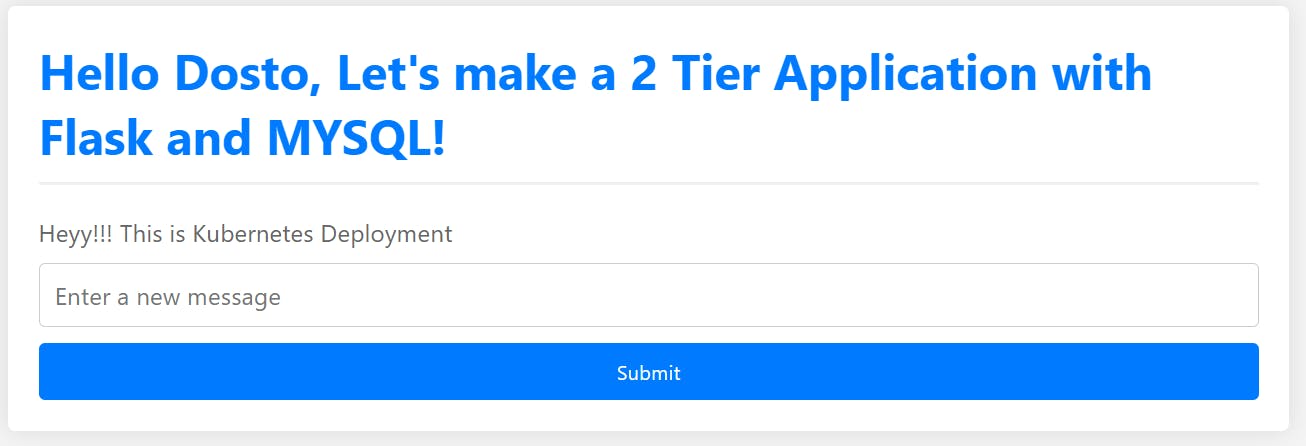
Step-7 Try to access your web app using node and node port:

Create some entries into it and verify with the database:
Now check it inside the Database:

++++++++++++++++THANK YOU++++++++++++++++++