Task-1:
Create a Service for your todo-app Deployment from Day-32
Create a Service definition for your todo-app Deployment in a YAML file.
Apply the Service definition to your K8 cluster using the
kubectl apply -f service.yml -n <namespace-name>command.Verify that the Service is working by accessing the todo-app using the Service's IP and Port in your Namespace.
Step-1 Create a deployment.yml file:

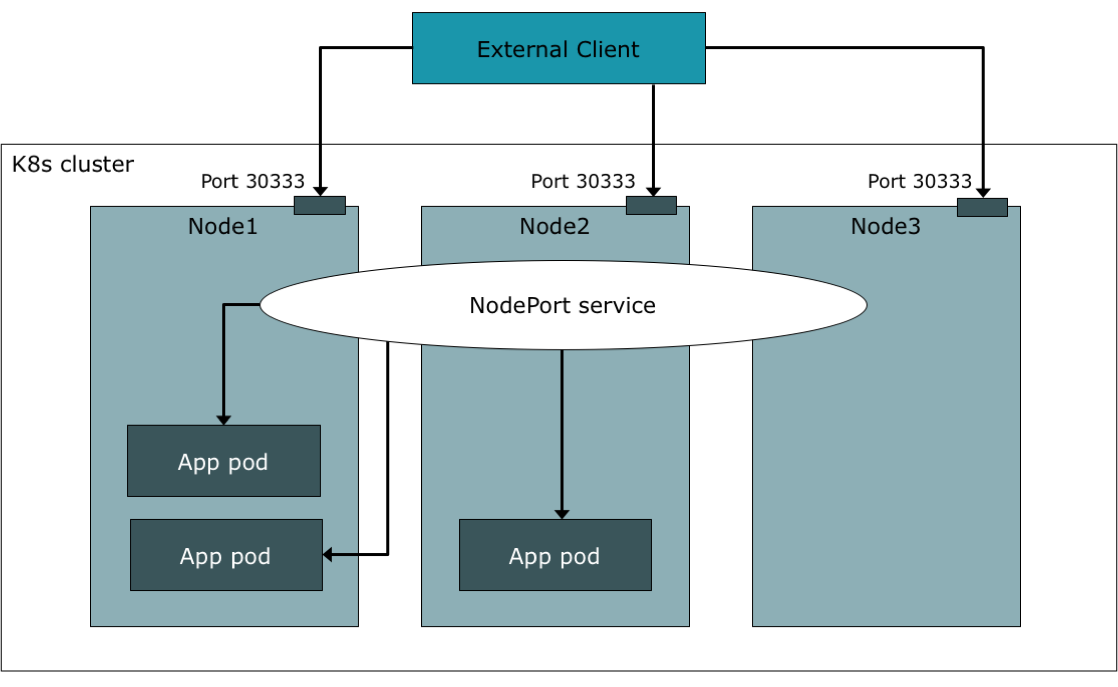
In this YAML file, we define a Service named todo-app-service that exposes the Deployment with the label app: todo-app. The Service is of type NodePort, which means it will be exposed on a static port on each Node in the cluster. We also specify that the Service should listen on port 80 and forward traffic to port 8080 on the Pods.
Apply this
kubectl apply -f deployment.yml

Step-2:
Create a service.yml file:

n this YAML file, we define a Service named todo-app-service that exposes the Deployment with the label app: todo-app. The Service is of type NodePort, which means it will be exposed on a static port on each Node in the cluster. We also specify that the Service should listen on port 80 and forward traffic to port 8000on the Pods.
Apply it
kubectl apply -f service.yml
Check it on Browser:



Task-2:
Create a ClusterIP Service for accessing the todo-app from within the cluster
Create a ClusterIP Service definition for your todo-app Deployment in a YAML file.
Apply the ClusterIP Service definition to your K8s (minikube) cluster using the
kubectl apply -f cluster-ip-service.yml -n <namespace-name>command.Verify that the ClusterIP Service is working by accessing the todo-app from another Pod in the cluster in your Namespace.
Step-1 Create a file cluster-ip-service.yml

Step-2 Apply the Service definition to the cluster using the following command:
kubectl apply -f cluster-ip-service.yml -n django-todo-ns

Step-3 Verify that the service is running by running the following command:

Step-4 Deploy another Pod in the django-todo-ns namespace to test the service. You can use the following YAML definition to create a simple Pod:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-pod
namespace: django-todo-ns
spec:
containers:
- name: busybox
image: busybox
command: ['sh', '-c', 'while true; do wget -q -O- django-todo-cluster-ip-service:8000; done']
This Pod runs a simple busybox container that repeatedly accesses the todo-app service using wget. The Pod should be able to access the django-todo-cluster-ip-service service using its name and port number.
Step-5 Apply the Pod definition using the following command:
kubectl apply -f test-pod.yml -n django-todo-ns

Step-6 Now enter into this pod :

kubectl exec -it test-pod -n django-todo-ns -- /bin/sh

St:ep-7 Test Todo app
wget -qO- http://10.96.190.151:8000

Now you sucessfuly Access it through another Port:
Task-3:
Create a LoadBalancer Service for accessing the todo-app from outside the cluster
Create a LoadBalancer Service definition for your todo-app Deployment in a YAML file.
Apply the LoadBalancer Service definition to your K8s (minikube) cluster using the
kubectl apply -f load-balancer-service.yml -n <namespace-name>command.Verify that the LoadBalancer Service is working by accessing the todo-app from outside the cluster in your Namespace.

Step-1 Create a YAML file named load-balancer-service.yml with the following contents:
This YAML file defines a Service named todo-app-lb that selects Pods with the label app: todo-app, exposes port 80 and forwards traffic to the Pod's http port. The type of the Service is set to LoadBalancer which will create an external load balancer in your cloud provider's infrastructure to route traffic to your service.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: django-todo
namespace: django-todo-ns
spec:
selector:
app: django-todo
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8000
type: LoadBalancer
Step-2 Apply the LoadBalancer Service definition to your K8s cluster using the following command:
kubectl apply -f load-balancer-service.yml -n django-todo-ns

- Verify that the LoadBalancer Service is working by accessing the todo-app from outside the cluster in your namespace.
You can get the external IP address of the LoadBalancer by running the following command:
kubectl get service todo-app-lb -n django-todo-ns
as External-ip is in pending state , wait for sometime untill it assigned:

I t can take time to get external IP meanwhile you can use Public DNS : port number


Note: The reason why the external IP was in a pending state is because Kubernetes needs to provision a load balancer from the cloud provider. Depending on the provider, this can take some time to complete. In some cases, the external IP address may never be provisioned due to issues with the provider or limitations of the Kubernetes cluster. In such cases, using the node instance Public IPv4 DNS with the specified port is a valid workaround.