Table of contents
- Docker:
- Installing Docker:
- Tasks:
- Use the docker run command to start a new container and interact with it through the command line.
- Use the docker inspect command to view detailed information about a container or image.
- Use the docker port command to list the port mappings for a container.
- Use the docker stats command to view resource usage statistics for one or more containers.
- Use the docker top command to view the processes running inside a container.
- Use the docker save command to save an image to a tar archive.
- Use the docker load command to load an image from a tar archive.
Docker:

Docker is an open-source platform for developing, packaging and deploying applications in a containerized environment. Containers are lightweight and portable virtual environments that can run on any system that supports Docker.
Docker provides a way to package an application and its dependencies into a container image, which can be easily shared and run on any system that supports Docker. Containers provide isolation between applications and their dependencies, allowing multiple applications to run on the same system without interfering with each other.
Installing Docker:
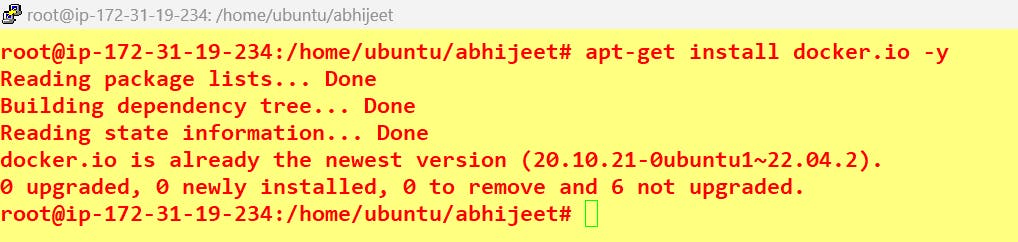
apt-get install docker.io -y
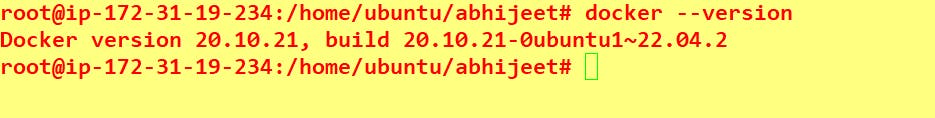
Check the version of Docker:
docker --version
Tasks:

Use the docker run command to start a new container and interact with it through the command line.
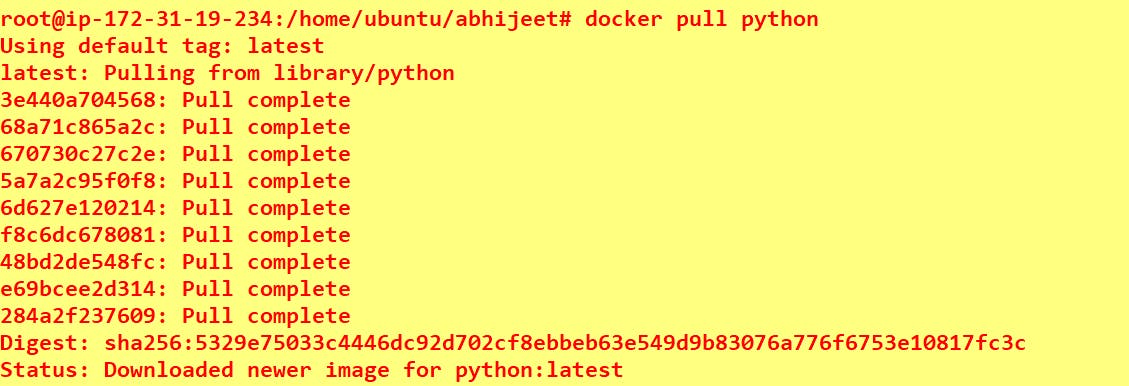
docker pull python
To check all images:
docker images
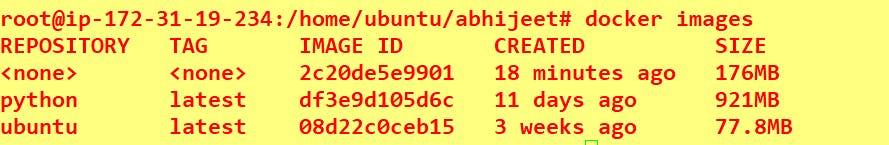
Create a container from the image:
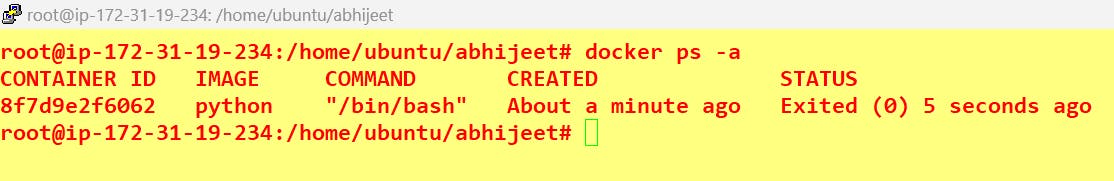
docker run -it <image name> /bin/bashTo see all containers:

docker ps -a
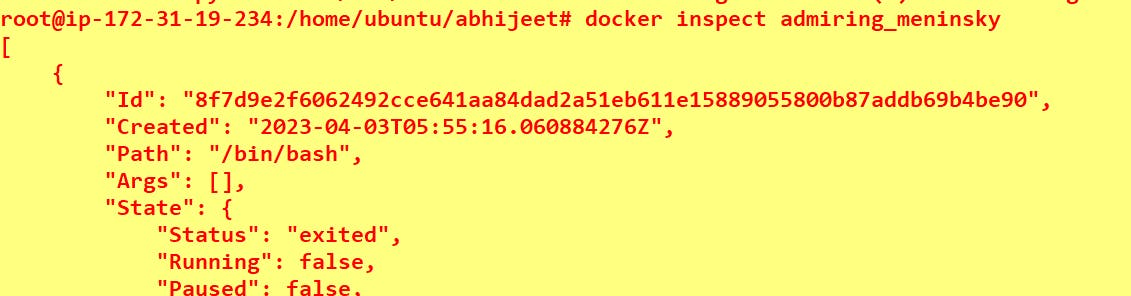
Use the docker inspect command to view detailed information about a container or image.
docker inspect <container name>
Use the docker port command to list the port mappings for a container.
docker port <container name >

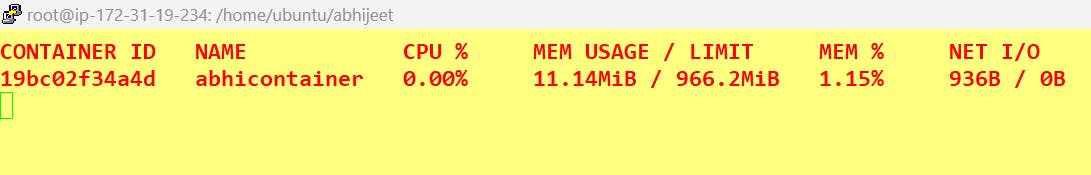
Use the docker stats command to view resource usage statistics for one or more containers.
docker stats <docker name>
Use the docker top command to view the processes running inside a container.
docker top <container name or id>

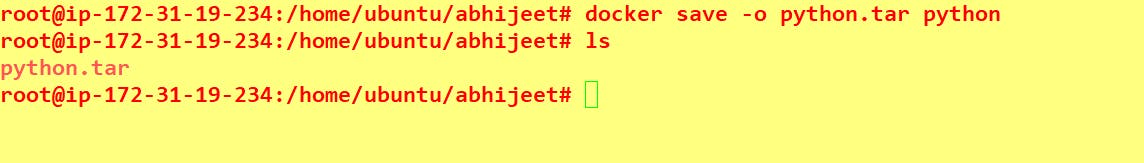
Use the docker save command to save an image to a tar archive.
docker save -o <image>.tar <image name>
Use the docker load command to load an image from a tar archive.
docker load -i <image.tar>

+++++++++++++++++++++++++++THANKYOU++++++++++++++++++++++++++
